AI Computer Control Agents: Transforming How We Interact With Technology
The Evolution of AI Computer Control Agents
The Evolution of AI Computer Control Agents
I've been fascinated by how rapidly AI computer control agents have evolved over the past few years. What began as simple automation tools has transformed into sophisticated AI systems capable of controlling computers just like humans do. Companies like OpenAI with their Operator, Anthropic's Claude, and Google's offerings aren't just creating new applications – they're fundamentally changing how we interact with technology.

The core technological advancements enabling these agents are truly remarkable. They can interpret visual information from screens, understand context, and control computer interfaces through mouse movements and keyboard inputs – just like a human would. What makes them fundamentally different from traditional automation is their ability to use reasoning capabilities rather than following fixed rule sets.
Historical Context
When I look back at the development path, it's clear we've come a long way from simple macros and scripts. The journey to today's ai agents capable of controlling computers has been marked by several key milestones:
Evolution of Computer Control Technologies
- 1980s-1990s: Simple keyboard macros and batch scripts
- 2000s: GUI automation tools that could interact with visual interfaces
- 2010s: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) with limited visual recognition
- 2020s: Breakthroughs in computer vision and natural language understanding
- Present: Full AI agents capable of reasoning about what they see and controlling interfaces
These developments wouldn't have been possible without massive advancements in computer vision that allow agents to "see" and understand screen contents, coupled with natural language understanding that helps them interpret human instructions. Together, these technologies have created a new paradigm in how we can delegate tasks to our digital assistants.
How AI Computer Control Agents Function
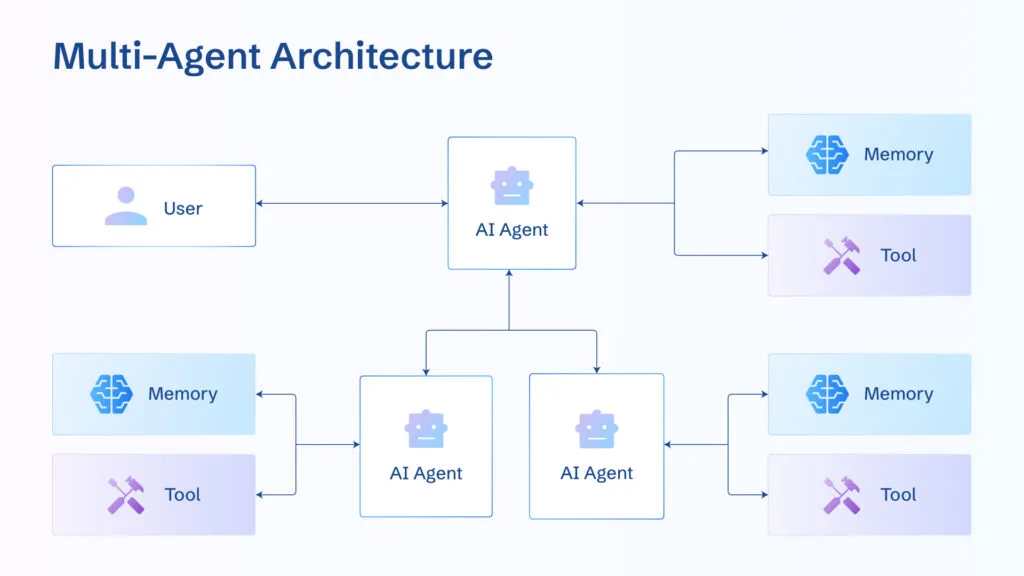
I find the technical foundations of how these agents operate to be absolutely fascinating. At their core, AI agents that control computers integrate three critical capabilities: computer vision, natural language processing, and sophisticated decision-making frameworks.
Core Components of AI Computer Control Agents
flowchart TD
User[User Request] --> NLP[Natural Language Processing]
NLP --> Intent[Intent Recognition]
Intent --> Planning[Task Planning]
Planning --> Vision[Computer Vision]
Vision --> UI[UI Element Recognition]
UI --> Decision[Decision Making]
Decision --> Action[Action Execution]
Action --> Feedback[Feedback Loop]
Feedback --> Vision
class User,NLP,Intent,Planning,Vision,UI,Decision,Action,Feedback fill:#FF8000,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
When I use PageOn.ai's AI Blocks approach to visualize these systems, I can see how users might customize and combine different control capabilities to suit their specific needs. This modular approach allows for incredible flexibility in how these agents can be deployed.
Core Technical Capabilities
Vision Systems
These agents use advanced computer vision to interpret screenshots, recognize text, buttons, icons, and other UI elements. They can understand both the structure and content of what's displayed on screen.
Decision Frameworks
Built on large language models, these frameworks determine appropriate actions based on visual input, user instructions, and understanding of common software interfaces.
Action Execution
The ability to control mouse movements, clicks, and keyboard inputs with precision, mimicking how a human would interact with interfaces.
Feedback Processing
Continuous monitoring of screen changes to verify actions worked as expected and adapt to unexpected outcomes.
One of the most impressive aspects is how these agents translate natural language instructions into specific computer operations. For example, when I tell an agent to "find the latest sales report and email it to the team," it needs to:
- Understand what a "sales report" might look like and where it might be located
- Navigate file systems or applications to locate it
- Identify the most recent version
- Open an email client
- Compose a message with appropriate context
- Attach the file
- Send to the right recipients
This level of coordination between vision, reasoning, and action execution represents a quantum leap beyond traditional automation. And with AI assistants becoming increasingly sophisticated, we're just beginning to see what's possible.
Real-World Applications Across Industries
I've been tracking the implementation of computer control agents across various industries, and the practical applications are truly impressive. These technologies aren't just theoretical – they're already transforming how businesses operate.
Take Atera's approach, for instance, where custom ai agents handle up to 40% of routine IT tasks autonomously. This isn't just incremental improvement – it's a fundamental shift in how IT departments function.
Industry Adoption of AI Computer Control Agents
Case Studies
IT Support Automation
An enterprise IT department deployed computer control agents to handle routine password resets and software installations, reducing ticket resolution time by 78% and freeing up IT staff for more complex issues.
ROI: $1.2M annual savings, 3-month implementation period
Financial Data Processing
A financial services firm uses AI agents to extract, validate, and process data from multiple financial systems, reducing manual data entry by 92% and virtually eliminating transcription errors.
ROI: 85% reduction in processing time, 99.7% accuracy rate
I've found that PageOn.ai's Deep Search capabilities significantly enhance these agents by finding and integrating relevant information directly into workflows. For example, in healthcare settings, agents can pull relevant patient history while a doctor is reviewing a case, or in logistics, they can automatically incorporate real-time traffic data into delivery planning.
Workflow Transformation with AI Control Agents
flowchart LR
subgraph Traditional ["Traditional Workflow"]
T1[Receive Request] --> T2[Manual Data Entry]
T2 --> T3[Human Processing]
T3 --> T4[Quality Check]
T4 --> T5[Delivery]
end
subgraph AIEnhanced ["AI-Enhanced Workflow"]
A1[Receive Request] --> A2[Automated Intake]
A2 --> A3[AI Processing]
A3 --> A4[Exception Handling]
A4 --> A5[Automated Delivery]
Human[Human Oversight] -.-> A3
Human -.-> A4
end
Traditional -.- AIEnhanced
What's particularly exciting is how these technologies are being adapted for industry-specific needs. In healthcare, they're helping with medical coding and documentation; in manufacturing, they're monitoring production systems and initiating maintenance protocols; in customer service, they're handling complex multi-system processes that previously required extensive human training.
Security and Safety Considerations
As someone deeply interested in the potential of AI computer control agents, I'm equally concerned about the security implications. Giving AI systems the ability to control our computers raises important questions about safety, privacy, and control.
Anthropic has specifically highlighted concerns around prompt injection attacks, where malicious actors might add something to a user's prompt to make the model take unexpected actions. As these agents can interpret screenshots from computers connected to the internet, they may be exposed to content containing such attacks.

I believe that secure ai agents require a multi-layered approach to safety. PageOn.ai's approach to visualization makes agent actions more transparent and understandable, which is crucial for building trust and ensuring safety.
Mitigating Risks
| Risk Category | Potential Threats | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Prompt Injection | Malicious content in screenshots or prompts that manipulate agent behavior | Input sanitization, content filtering, action confirmation for high-risk operations |
| Data Exposure | Sensitive information visible in screenshots sent to AI systems | Automatic PII detection, data masking, local processing options |
| Unauthorized Actions | Agents performing actions beyond intended scope | Permission systems, action logging, human approval workflows |
| System Vulnerabilities | Exploitation of underlying system access | Sandboxing, least privilege principles, secure authentication |
Multi-Layer Security Framework
flowchart TD
User[User Request] --> InputFilter[Input Filtering]
InputFilter --> IntentAnalysis[Intent Analysis]
IntentAnalysis --> RiskAssess[Risk Assessment]
RiskAssess -->|Low Risk| DirectExec[Direct Execution]
RiskAssess -->|Medium Risk| ConfirmExec[Confirmation Required]
RiskAssess -->|High Risk| HumanApproval[Human Approval]
DirectExec --> Monitoring[Real-time Monitoring]
ConfirmExec --> Monitoring
HumanApproval --> Monitoring
Monitoring --> Logging[Comprehensive Logging]
Monitoring -->|Anomaly Detected| Intervention[Automatic Intervention]
style User fill:#f9f9f9,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
style InputFilter fill:#ffebcc,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
style IntentAnalysis fill:#ffebcc,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
style RiskAssess fill:#ffebcc,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
style DirectExec fill:#d4edda,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
style ConfirmExec fill:#fff3cd,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
style HumanApproval fill:#f8d7da,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
style Monitoring fill:#d1ecf1,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
style Logging fill:#d1ecf1,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
style Intervention fill:#f8d7da,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
I think one of the most critical aspects of implementing these agents safely is maintaining appropriate human oversight. The best implementations I've seen maintain a balance where:
- High-risk actions require explicit human approval
- Medium-risk actions prompt for confirmation
- Only routine, low-risk actions proceed automatically
- All actions are logged for accountability and review
- Clear intervention mechanisms exist to halt agent activity when needed
By implementing these safety measures and using visualization tools like those offered by PageOn.ai, organizations can significantly reduce the risks while still benefiting from the productivity improvements these agents offer.
The Future Landscape of AI Computer Control
When I look at where AI computer control agents are headed in the next 3-5 years, I see a landscape of tremendous opportunity and transformation. The technology is advancing at a breathtaking pace, with each iteration becoming more capable and versatile.

One of the most exciting developments I'm tracking is the move toward universal interfaces that work across all digital environments. OpenAI has specifically mentioned making their Computer-Using Agent (CUA) available via API, which will allow developers to build their own computer-using agents. This democratization of the technology will lead to an explosion of specialized agents designed for specific industries and use cases.
Emerging Trends
Projected Growth in AI Agent Capabilities
I'm particularly interested in how PageOn.ai's Agentic capabilities could transform how users express their intentions to computer control agents. By providing intuitive visual interfaces for configuring and monitoring agents, PageOn.ai could make these powerful tools accessible to non-technical users.
API-First Development
The move toward making agent technologies available through APIs will enable a new ecosystem of developers to create specialized solutions for specific industries and use cases.
Democratized Creation
No-code platforms will allow non-technical users to create and customize their own AI agents, significantly expanding the adoption and application of these technologies.
Extended Reality Integration
AI agents will expand beyond traditional computing interfaces to work seamlessly with AR/VR environments, creating new possibilities for immersive, AI-assisted experiences.
Evolution of Professional Roles with AI Agents
flowchart TD
subgraph Present ["Present Day"]
P1[Routine Tasks] --> P2[Technical Tasks]
P2 --> P3[Creative & Strategic Work]
P1 --> Human1[Human Workers]
P2 --> Human1
P3 --> Human1
end
subgraph Future ["5 Years From Now"]
F1[Routine Tasks] --> F2[Technical Tasks]
F2 --> F3[Creative & Strategic Work]
F1 --> Agent[AI Agents]
F2 --> Collaboration[Human-AI Collaboration]
F3 --> Human2[Human Focus]
end
Present -.- Future
I believe these developments will fundamentally reshape professional roles and workflows. Rather than replacing humans, the most successful implementations will augment human capabilities, handling routine tasks while enabling people to focus on higher-value creative and strategic work. This shift will require new skills – particularly around effectively directing and collaborating with AI systems – but has the potential to dramatically increase productivity and job satisfaction.
Getting Started with AI Computer Control Agents
As I've explored the world of AI computer control agents, I've developed some practical guidance for organizations looking to evaluate and implement these technologies. The landscape is evolving rapidly, but there are clear best practices emerging.
When choosing between different AI agent platforms, I recommend considering several key factors:
Safety & Security Features
Look for platforms with robust permission systems, action logging, and approval workflows for sensitive operations.
Integration Capabilities
Ensure the platform can connect with your existing software ecosystem and handle the specific applications you use.
Customization Options
Assess how easily you can tailor the agent's capabilities and behaviors to your specific workflows and requirements.
Transparency & Explainability
Prioritize solutions that make agent actions visible and understandable to build trust and enable effective oversight.
I've found that PageOn.ai's visualization capabilities are particularly valuable in the planning stages, helping teams map out potential agent workflows before implementation. This visual approach makes it easier to identify potential issues, optimize processes, and build stakeholder buy-in.
Implementation Strategies
Phased Implementation Approach
flowchart LR
A[Assessment Phase] --> B[Pilot Implementation]
B --> C[Controlled Expansion]
C --> D[Full Deployment]
subgraph A1[Assessment Activities]
A1a[Process Mapping]
A1b[Task Selection]
A1c[ROI Analysis]
end
subgraph B1[Pilot Activities]
B1a[Limited Scope Testing]
B1b[User Feedback]
B1c[Performance Metrics]
end
subgraph C1[Expansion Activities]
C1a[Refined Workflows]
C1b[Additional Use Cases]
C1c[Training Programs]
end
subgraph D1[Full Deployment]
D1a[Integration with Core Systems]
D1b[Continuous Improvement]
D1c[Governance Framework]
end
A --- A1
B --- B1
C --- C1
D --- D1
For successful adoption, I recommend following these best practices:
- Start small and focused with clearly defined use cases that have measurable outcomes
- Involve end users early in the selection and configuration process
- Create clear governance frameworks defining what agents can and cannot do
- Establish monitoring protocols to track agent actions and outcomes
- Develop training programs to help employees effectively collaborate with AI agents
- Implement feedback mechanisms to continuously improve agent performance
When measuring success, I look at both quantitative metrics (time saved, error reduction, cost savings) and qualitative factors (user satisfaction, reduced stress, increased focus on high-value work). The most successful implementations I've seen are those that approach agents as team members rather than just tools – thinking carefully about how they fit into existing workflows and team dynamics.
Key Success Metrics for AI Agent Implementation
By taking a thoughtful, phased approach to implementation and focusing on both technical capabilities and human factors, organizations can successfully integrate AI computer control agents into their operations, realizing significant benefits while managing potential risks.
Transform Your Visual Expressions with PageOn.ai
Ready to visualize complex AI agent workflows and make them more understandable? PageOn.ai provides powerful tools to create clear, intuitive visualizations that help you design, explain, and implement AI computer control agents effectively.
Final Thoughts
As I've explored the fascinating world of AI computer control agents, I've been struck by how quickly this technology is evolving and how profound its impact will be. These agents represent not just incremental improvements to automation but a fundamental shift in how we interact with computers and digital systems.
While challenges around security, privacy, and appropriate human oversight remain, the potential benefits in terms of productivity, accessibility, and user experience are enormous. I believe we're just beginning to understand what's possible when AI can truly see and interact with our digital world the way humans do.
For organizations looking to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape, tools like PageOn.ai that help visualize, understand, and communicate complex AI workflows will be invaluable. By making the abstract concrete and the complex clear, such visualization capabilities will help ensure that AI computer control agents deliver on their promise while remaining safe, transparent, and aligned with human needs.
You Might Also Like
Transform Your Google Slides: Advanced Techniques for Polished Presentations
Master advanced Google Slides techniques for professional presentations. Learn design fundamentals, visual enhancements, Slide Master, and interactive elements to create stunning slides.
Building New Slides from Prompts in Seconds | AI-Powered Presentation Creation
Discover how to create professional presentations instantly using AI prompts. Learn techniques for crafting perfect prompts that generate stunning slides without design skills.
Revolutionizing Slide Deck Creation: How AI Tools Transform Presentation Workflows
Discover how AI-driven tools are transforming slide deck creation, saving time, enhancing visual communication, and streamlining collaborative workflows for more impactful presentations.
Mastering Content Rewriting: How Gemini's Smart Editing Transforms Your Workflow
Discover how to streamline content rewriting with Gemini's smart editing capabilities. Learn effective prompts, advanced techniques, and workflow optimization for maximum impact.