The Evolution of Low-Code AI Agents
Transforming Business Development Without Deep Technical Expertise
The world of AI development is undergoing a dramatic transformation. Once the exclusive domain of specialized developers and data scientists, AI agent creation is now accessible to business users through intuitive low-code platforms that minimize or eliminate complex programming requirements.
Understanding Low-Code AI Agents: The Fundamentals
When I first encountered the concept of AI agents, I was struck by their transformative potential. These autonomous software systems can learn, adapt, and reason to carry out tasks without constant human direction, opening up a world of possibilities for businesses of all sizes.

What's truly revolutionary is how low-code platforms are democratizing AI agent creation. By minimizing or eliminating the need for complex coding, these platforms are making powerful AI capabilities accessible to business users without deep technical expertise. This democratization is similar to how website builders transformed web development decades ago.
Key Components of Low-Code AI Agents
flowchart TD
A[AI Agent] --> B[NLP Capabilities]
A --> C[Workflow Automation]
A --> D[Integration Abilities]
B --> B1[Intent Recognition]
B --> B2[Response Generation]
C --> C1[Visual Workflow Builder]
C --> C2[Logic Processing]
D --> D1[API Connectors]
D --> D2[Data Source Integration]
classDef orange fill:#FF8000,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px,color:white;
class A orange
A modern low-code AI agent typically consists of three essential components:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Capabilities: Enabling the agent to understand and generate human language, facilitating intuitive interactions.
- Workflow Automation Features: Allowing the agent to execute predefined processes and make decisions based on inputs and conditions.
- Integration Abilities: Connecting the agent to existing business systems, databases, and external services to access and manipulate data.
Low-Code vs. No-Code Approaches
| Feature | Low-Code | No-Code |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Expertise Required | Minimal coding knowledge | No coding knowledge |
| Customization Potential | High - can extend with code | Limited to platform capabilities |
| Development Speed | Fast | Very fast |
| Typical Users | Business analysts, citizen developers | Business users, non-technical staff |
PageOn.ai's visual building blocks approach aligns perfectly with modern low-code development principles. By offering intuitive tools that allow users to construct complex visualizations without dealing with layout complexities, PageOn.ai embodies the same democratizing spirit that's driving the low-code AI agent revolution.
Just as ai agents are becoming accessible to non-technical users, PageOn.ai's approach to visualization makes complex information design accessible to those without graphic design expertise.
The Business Value Proposition of Low-Code AI Agents
In my experience working with various organizations, I've seen firsthand how low-code AI agents are transforming business operations. These solutions bridge the critical gap between business needs and technical execution, allowing ideas to move from concept to implementation without lengthy development cycles.

Development Time Reduction
The data speaks for itself: organizations implementing low-code AI agents typically see an 80% reduction in development time compared to traditional coding approaches. This acceleration enables businesses to respond more quickly to market changes and customer needs.
Cost-Efficiency Benefits
For organizations with limited technical resources, the cost benefits are substantial. Low-code platforms eliminate the need for specialized AI developers, who command premium salaries in today's market. Additionally, the rapid development cycles reduce the overall project costs and allow for faster realization of ROI.
Case Study: A mid-sized insurance company implemented a low-code AI agent for claims processing, reducing processing time by 65% and saving approximately $450,000 annually in operational costs. The entire development process took just 6 weeks from concept to deployment.
PageOn.ai's "Turn Fuzzy Thought into Clear Visuals" approach parallels this value proposition by helping business users conceptualize complex workflows without technical barriers. When designing AI agent processes, this visualization capability becomes invaluable for communicating ideas between business stakeholders and implementation teams.
By implementing AI agents through low-code platforms, businesses can achieve remarkable ROI metrics across multiple dimensions, from development speed to user adoption rates.
Key Capabilities of Modern Low-Code AI Agent Platforms
Today's low-code AI agent platforms offer a robust set of capabilities that enable non-technical users to create sophisticated AI solutions. I've found that understanding these core features helps organizations select the right platform for their specific needs.

Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) capabilities form the foundation of intuitive human-agent interactions. Modern low-code platforms integrate sophisticated NLP models that can understand context, sentiment, and intent from user inputs. This enables the creation of conversational agents that feel natural and responsive.
Auto-Generation of Functional Modules
flowchart LR
A[Business User] -->|"Provides prompt: 'Create a customer onboarding process'"| B[Low-Code Platform]
B --> C{Auto-Generation Engine}
C -->|Analyzes intent| D[Generated Components]
D --> D1[Form Builder]
D --> D2[Email Notification]
D --> D3[Data Storage]
D --> D4[Verification Logic]
D1 & D2 & D3 & D4 --> E[Complete Functional Module]
E -->|Ready for customization| F[Business User]
classDef orange fill:#FF8000,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px,color:white;
class C orange
One of the most impressive capabilities I've seen is the auto-generation of functional modules based on simple prompts. Users can describe what they need in plain language, and the platform will assemble the necessary components to create a working solution. This dramatically accelerates development and reduces the learning curve.
Integration Capabilities
Modern low-code platforms excel at connecting with existing business systems and data sources. Through pre-built connectors and API integration tools, these platforms allow AI agents to access and manipulate data from CRM systems, databases, cloud services, and other business applications without complex coding.
Visual Workflow Builders
Visual workflow builders with drag-and-drop interfaces are the hallmark of low-code AI agent platforms. These intuitive tools allow users to design complex process flows by connecting visual elements that represent actions, decisions, and data operations. The resulting workflows are both easy to create and simple to understand.
PageOn.ai's AI Blocks feature exemplifies this approach to visual creation. By enabling fluid combination of content and structure without layout complexities, PageOn.ai allows users to focus on the logic and flow of their visualizations rather than technical implementation details.
For businesses looking to implement custom ai agents, these capabilities provide the foundation for creating tailored solutions that address specific business needs without requiring extensive development resources.
Popular Low-Code AI Agent Development Platforms
The market for low-code AI agent platforms is growing rapidly, with several strong contenders offering unique approaches and capabilities. In my work with various organizations, I've had the opportunity to evaluate many of these platforms firsthand.
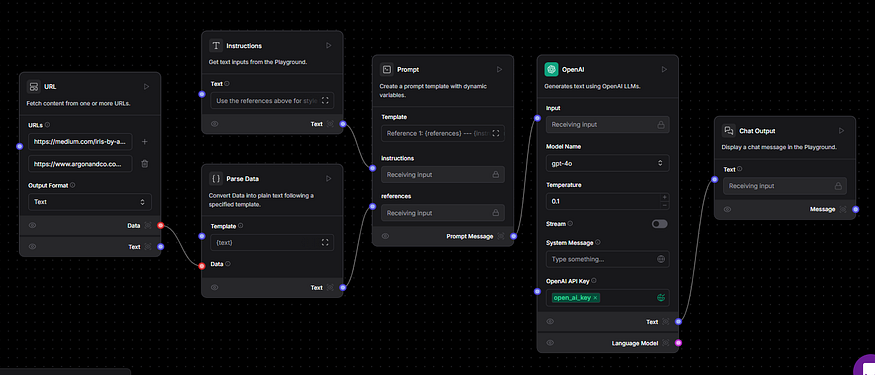
Visual Builder Platforms
Gumloop
A no-code tool focused on helping users visually create and deploy AI agents through a drag-and-drop canvas.
- Intuitive flowchart-style interface
- Strong focus on workflow automation
- Described as "if Zapier and ChatGPT had a baby"
- Free plan available with paid plans starting at $97/month
Langflow
A Python-based platform designed for building AI applications with a focus on single-agent systems and RAG.
- Open-source foundation
- Strong integration with LangChain
- Support for multiple AI frameworks (OpenAI, Hugging Face, TensorFlow)
- Ideal for AI-centric workflows
Flowise
A visual editor with LangChain-style abstractions for integrating different LLM models and custom tools.
- Flexible model integration
- Support for custom tools and extensions
- Open-source with active community
- Strong focus on LLM orchestration
Enterprise Platforms
Microsoft Copilot Studio
A platform for creating and deploying AI agents with strong Microsoft ecosystem integration.
- Seamless integration with Microsoft 365
- Specialized for customer queries and sales lead identification
- Customizable "AI employees" concept
- Strong enterprise security features
Google's Vertex AI Agent Builder
Google Cloud's low-code platform for building and deploying conversational agents through a web-based interface.
- Visual design of LLM-powered workflows
- Native Google Cloud integration
- Strong scalability features
- Support for custom APIs and system instructions
IBM's AgentLab
Part of the Watsonx.ai suite, offering a low-code, drag-and-drop editor for building tailored agents.
- Enterprise-focused security and compliance (RBAC, GDPR, HIPAA)
- Comprehensive governance tools
- Highly customizable for specific business needs
- Integration with IBM's broader AI ecosystem
PageOn.ai's approach to visual content generation and agent design offers a unique perspective compared to these platforms. While traditional low-code AI platforms focus on process automation and decision logic, PageOn.ai emphasizes the visual representation and communication of complex ideas – a critical component when designing and explaining AI agent workflows.
For organizations looking to implement AI solutions, understanding the strengths of each platform is essential. The integration of ai coding assistants can further enhance the development process, especially when some customization is required beyond what the low-code platform provides.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
In my work across different industries, I've witnessed low-code AI agents transforming operations in numerous ways. The flexibility and accessibility of these platforms have enabled businesses to implement AI solutions that were previously beyond their technical capabilities.

Customer Service and Support Automation
One of the most common and immediately impactful applications I've seen is in customer service. Low-code AI agents can handle routine inquiries, process support tickets, and even resolve common issues without human intervention. This not only reduces operational costs but also improves response times and customer satisfaction.
flowchart TD
A[Customer Query] --> B[AI Agent]
B --> C{Query Analysis}
C -->|Simple Question| D[Automated Response]
C -->|Complex Issue| E[Human Agent Handoff]
C -->|Account Specific| F[Retrieve Customer Data]
F --> G[Personalized Solution]
D & G --> H[Resolution]
E --> I[Human Agent]
I --> H
classDef orange fill:#FF8000,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px,color:white;
class B,C orange
Business Process Automation
Routine operational tasks across departments are prime candidates for low-code AI agent automation. From invoice processing and approval workflows to employee onboarding and IT service management, these agents can handle structured processes with minimal human oversight.
Case Study: A manufacturing company implemented a low-code AI agent to manage their procurement approval process. The agent automatically routes requests, checks budget allocations, and only escalates exceptions to human managers. This reduced approval times from 3 days to 4 hours and freed up 25% of procurement staff time.
Data Analysis and Insight Generation
Low-code AI agents excel at continuous data monitoring and analysis tasks that would be impractical for humans to perform. These agents can process large volumes of data, identify patterns or anomalies, and generate actionable insights without requiring data science expertise.
Sales and Marketing Automation
In sales and marketing, low-code AI agents can qualify leads, personalize outreach, and orchestrate multi-channel campaigns. These agents can analyze customer behavior, adapt messaging based on engagement, and provide sales teams with prioritized opportunities.
PageOn.ai's Deep Search capability enhances these AI agent applications by finding and integrating relevant visuals and data directly into workflows. This is particularly valuable when creating customer-facing communications or internal reports that need to convey complex information clearly.
Successful ai implementation across these use cases requires thoughtful planning and clear communication of capabilities and limitations to stakeholders.
Building Your First Low-Code AI Agent: A Step-by-Step Framework
Having guided several teams through their first low-code AI agent projects, I've developed a framework that helps ensure success. This structured approach keeps projects focused and increases the likelihood of delivering real business value.
.svg)
Step 1: Define Your Agent's Purpose
Begin by clearly defining what your AI agent will do and how success will be measured. Specificity is crucial here—avoid vague goals like "improve customer service" in favor of specific objectives like "reduce first-response time for customer inquiries by 50%."
Key Questions to Answer:
- What specific task or process will the agent handle?
- Who are the primary users or beneficiaries?
- What metrics will determine success?
- What are the boundaries of the agent's responsibilities?
Step 2: Select the Appropriate Platform
Choose a low-code platform that aligns with your technical capabilities, integration needs, and long-term goals. Consider factors such as existing technology investments, team familiarity, and specific features required for your use case.
flowchart TD
A[Platform Selection] --> B{Technical Expertise?}
B -->|None| C[No-Code Platform]
B -->|Limited| D[Low-Code Platform]
B -->|Substantial| E[Code-Extensible Platform]
C & D & E --> F{Enterprise Integration?}
F -->|Microsoft Ecosystem| G[Microsoft Copilot Studio]
F -->|Google Cloud| H[Vertex AI]
F -->|IBM/Enterprise| I[IBM AgentLab]
F -->|Independent/Startup| J[Gumloop/Langflow/Flowise]
G & H & I & J --> K{Primary Use Case?}
K -->|Customer Service| L[Conversational Focus]
K -->|Process Automation| M[Workflow Focus]
K -->|Data Analysis| N[Analytics Focus]
classDef orange fill:#FF8000,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px,color:white;
class A,F,K orange
Step 3: Design the Agent's Workflow
Use the visual interfaces provided by your chosen platform to map out the agent's workflow. Start with a simple flow that addresses the core functionality, then iteratively add complexity as you test and refine.
This is where PageOn.ai's conversational creation approach can be particularly valuable. By allowing you to articulate your workflow needs in natural language and then converting those descriptions into clear visual representations, PageOn.ai helps bridge the gap between concept and implementation.
Step 4: Integrate Data Sources and APIs
Connect your agent to the necessary data sources and external services. Most low-code platforms provide pre-built connectors for common systems, but you may need to configure custom API integrations for specialized tools.
Step 5: Test and Refine
Implement a thorough testing process that covers both expected and edge-case scenarios. Gather feedback from actual users and iteratively refine the agent's functionality, conversational abilities, and decision-making logic.
Pro Tip: Start with a limited pilot deployment that addresses a specific subset of your target use case. This allows you to gather real-world feedback and make adjustments before scaling to a broader implementation.
Throughout this process, effective visualization of the agent's workflow and decision paths is crucial for stakeholder understanding and alignment. PageOn.ai's ability to transform complex processes into clear visuals helps ensure that everyone involved shares a common understanding of how the agent will function.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Low-Code AI Agent Development
While low-code AI agent platforms significantly reduce technical barriers, they come with their own set of challenges. In my experience implementing these solutions, I've encountered several common obstacles that teams should be prepared to address.
Integration Limitations with Legacy Systems
One of the most significant challenges is connecting low-code AI agents to older, legacy systems that lack modern APIs or integration points. These systems often contain critical business data but weren't designed with modern integration patterns in mind.
Strategies for Legacy Integration:
- Implement middleware or API gateway solutions that can translate between modern and legacy protocols
- Use robotic process automation (RPA) to interact with legacy systems through their user interfaces
- Create scheduled data synchronization processes that update a modern database from legacy sources
- Evaluate the cost-benefit of modernizing critical legacy components versus working around their limitations
Managing Expectations Around AI Capabilities
The term "AI" often creates inflated expectations about what these systems can actually do. Business stakeholders may expect human-like reasoning or perfect accuracy, when in reality, AI agents have specific limitations and operate best within well-defined boundaries.
Ensuring Proper Data Governance and Security
Low-code platforms often abstract away the underlying data handling, which can create challenges for organizations with strict data governance requirements. Ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA requires careful configuration and monitoring.
Organizations must implement proper access controls, data encryption, and audit trails even when using simplified low-code interfaces. This often requires collaboration between business users and IT security teams to ensure compliance.
Balancing Customization Needs with Platform Constraints
Low-code platforms inevitably involve trade-offs between ease of use and customization flexibility. As projects evolve, teams often encounter specific requirements that push against the boundaries of what their chosen platform can accomplish without custom code.
flowchart TD
A[Customization Need Identified] --> B{Within Platform Capabilities?}
B -->|Yes| C[Implement Using Platform Tools]
B -->|No| D{Critical Requirement?}
D -->|Yes| E[Consider Custom Code Extension]
D -->|No| F[Adjust Requirements or Workflow]
E --> G{Platform Supports Extensions?}
G -->|Yes| H[Develop Custom Component]
G -->|No| I[Evaluate Platform Change]
classDef orange fill:#FF8000,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px,color:white;
class B,D,G orange
PageOn.ai's agentic approach helps address these challenges by transforming user intent into polished, unique visual solutions. This flexibility allows teams to create custom visualizations that accurately represent their specific workflows, even when those workflows push the boundaries of what traditional low-code platforms can represent.
By anticipating and planning for these common challenges, organizations can significantly increase their chances of successful low-code AI agent implementation.
Future Trends in Low-Code AI Agent Development
The field of low-code AI agent development is evolving rapidly, with several emerging trends that promise to further transform how organizations build and deploy these solutions. Based on my observations of the market and conversations with industry leaders, here are the key developments to watch.

The Growing Role of Multimodal AI
Current low-code AI agents primarily process text and structured data, but the next generation will increasingly incorporate multimodal capabilities—understanding and generating images, audio, video, and other media formats. This will dramatically expand the range of use cases and the richness of interactions.
Imagine customer service agents that can analyze uploaded photos of damaged products, or sales agents that can generate personalized video presentations based on prospect data. These capabilities are beginning to emerge in specialized tools and will soon be integrated into mainstream low-code platforms.
Expansion of Enterprise-Grade Features
As low-code AI adoption grows in larger organizations, platforms are enhancing their enterprise capabilities. This includes more robust governance features, advanced security controls, comprehensive audit trails, and integration with enterprise identity management systems.
Industry Insight: IBM's AgentLab exemplifies this trend with its focus on enterprise compliance features like RBAC, GDPR compliance, and HIPAA readiness. We can expect other platforms to follow suit as they compete for enterprise adoption.
Increasing Autonomy and Decision-Making Abilities
Future low-code AI agents will feature greater autonomy and more sophisticated decision-making capabilities. Rather than following rigid, pre-defined workflows, these agents will dynamically adapt their behavior based on context, historical patterns, and real-time data analysis.
Convergence with Specialized AI Tools
We're beginning to see convergence between general-purpose low-code platforms and specialized AI tools. Platforms are incorporating capabilities like computer vision, advanced natural language processing, and predictive analytics that were previously only available through separate, specialized solutions.
This trend will accelerate, creating more powerful and versatile low-code environments where business users can access sophisticated AI capabilities without switching between multiple tools or platforms.
PageOn.ai is well-positioned to evolve alongside these trends with its focus on turning fuzzy thought into clear visuals. As AI agents become more complex and autonomous, the need for intuitive visualization of their capabilities and decision processes will only increase. PageOn.ai's approach to visual content creation provides an elegant solution to this growing challenge.
Conclusion: Democratizing AI Through Low-Code Development
Throughout this exploration of low-code AI agent development, we've seen how these platforms are fundamentally transforming who can create AI solutions and how quickly they can be deployed. This democratization of AI development represents a significant shift in how organizations approach digital transformation.

The rise of "citizen developers" empowered by these tools is particularly noteworthy. Business users with domain expertise but limited technical skills can now create sophisticated AI solutions that address specific operational challenges. This shift not only accelerates development but often results in solutions that are better aligned with actual business needs.
For most organizations, the optimal approach lies in finding the right balance between buying pre-built solutions and customizing for specific needs. Low-code platforms offer a middle ground, providing the foundation and basic building blocks while allowing for tailored configurations that address unique requirements.
As we look to the future, it's clear that low-code AI development will continue to evolve and expand. The platforms will become more powerful, the integration capabilities more seamless, and the resulting agents more autonomous and intelligent. Organizations that embrace these tools now will be well-positioned to leverage these advancements as they emerge.
PageOn.ai's approach to visual content creation parallels this democratization happening in AI agent development. By making it easier for anyone to transform complex ideas into clear, compelling visuals, PageOn.ai empowers the same business users who are leveraging low-code AI platforms to better communicate their solutions and insights.
The future of AI belongs not just to specialized developers, but to everyone with ideas and challenges to solve. Low-code platforms are the bridge making this future accessible today.
Transform Your Visual Expressions with PageOn.ai
Ready to create stunning visualizations that bring your AI agent workflows to life? PageOn.ai makes it easy to turn complex ideas into clear, compelling visuals that anyone can understand.
Start Creating with PageOn.ai TodayYou Might Also Like
Revolutionizing Slide Deck Creation: How AI Tools Transform Presentation Workflows
Discover how AI-driven tools are transforming slide deck creation, saving time, enhancing visual communication, and streamlining collaborative workflows for more impactful presentations.
Transforming Presentations: Strategic Use of Color and Imagery for Maximum Visual Impact
Discover how to leverage colors and images in your slides to create visually stunning presentations that engage audiences and enhance information retention.
Mastering Visual Flow: How Morph Transitions Transform Presentations | PageOn.ai
Discover how Morph transitions create dynamic, seamless visual connections between slides, enhancing audience engagement and transforming ordinary presentations into memorable experiences.
The Art of Text Contrast: Transform Audience Engagement With Visual Hierarchy
Discover how strategic text contrast can guide audience attention, enhance information retention, and create more engaging content across presentations, videos, and marketing materials.