50 Examples of Present and Past Tense Words
Master verb tenses to enhance your English communication skills
Understanding verb tenses is crucial in mastering any language. You often encounter the present and past tenses, which form the backbone of English communication. The simple present tense alone accounts for over 57% of verbs used in speech, while the simple past follows closely. Grasping these tenses helps you express actions clearly and accurately. This blog post aims to provide you with practical examples of present to past tense words, enhancing your language skills and confidence.
Understanding Verb Tenses
Understanding verb tenses is essential in mastering English. You use tenses to express time-related actions, making your communication clear and precise. Let's explore the present and past tenses, which are fundamental in any language.
Verb Tense Usage in English
The following chart shows the frequency of different verb tenses in everyday communication:
What is Present Tense?
Definition and Usage
The present tense describes actions happening now or regularly. In English, it often uses the base form of the verb. You might say, "I walk to school," to indicate a habitual action. This tense helps you convey facts, routines, and general truths.
Examples of Present Tense Verbs
Consider these examples:
- "I read every morning."
- "She plays the piano beautifully."
- "They learn new skills quickly."
These sentences illustrate how the present tense functions in everyday language.
What is Past Tense?
Definition and Usage
The past tense refers to actions that have already occurred. In English, it typically involves adding -ed to regular verbs or changing the form for irregular verbs. You use this tense to narrate events or describe completed actions.
Examples of Past Tense Verbs
Here are some examples:
- "I walked to the store yesterday."
- "He read the book last night."
- "They learned about history in class."
AE Maetzner divided tenses into simple and compound forms, influencing modern linguists' understanding of tense structures. English has only two morphological tenses: present and past, marked with specific suffixes or changes in the verb form.
Understanding these tenses enhances your ability to express yourself clearly. By mastering present and past tenses, you build a strong foundation for more complex structures like tense vs future perfect.
Present Past Past Participle
Understanding the transition from present to past tense words is essential for mastering English verb forms. This section will guide you through commonly used verbs and their transformations, including the past participle forms.
Verb Transformation Process
Below is a visualization of how verbs transform across different tenses:
flowchart LR
A[Base Form] -->|Regular Verb| B[Add -ed/-d]
A -->|Irregular Verb| C[Unique Change]
B --> D[Past Tense]
C --> D
D -->|Regular Verb| E[Add -ed/-d + have/has/had]
D -->|Irregular Verb| F[Unique Form + have/has/had]
E --> G[Past Participle]
F --> G
Present to Past Tense Words
Commonly Used Present Tense Verbs
In English, you frequently use present tense verbs to describe actions happening now or regularly. These verbs form the foundation of your daily communication. Here are some common words you might encounter:
- Walk: You say, "I walk to school every day."
- Help: You express, "I help my friend with homework."
- Learn: You state, "I learn new things quickly."
These examples illustrate how present tense verbs function in everyday language, providing clarity and immediacy to your statements.
Commonly Used Past Tense Verbs
When discussing actions that have already occurred, you switch to past tense verbs. This change often involves adding -ed to regular verbs or altering the form for irregular verbs. Consider these examples:
- Walked: You narrate, "I walked to the store yesterday."
- Helped: You recount, "I helped my friend last week."
- Learned: You describe, "I learned about history in class."
These past tense verbs allow you to effectively communicate events that have taken place, offering a clear timeline of actions.
Present Continuous Tense
Definition and Examples
The present continuous tense describes actions currently in progress. It combines the present tense of the verb "to be" with the present participle form of the main verb. This tense helps you convey ongoing activities. For instance:
- Walking: You say, "I am walking to the park now."
- Helping: You express, "I am helping my sister with her project."
- Learning: You state, "I am learning to play the guitar."
Understanding the present, past, and past participle forms of verbs enriches your language skills. By mastering these forms, you enhance your ability to express time-related actions accurately. A list encompassing present and past participle forms can serve as a valuable resource in your language learning journey.
List of Present Tense Words

Understanding present tense verbs is essential for clear communication. You use them to describe actions happening now or regularly. This section provides a concise list of regular and irregular verbs, helping you grasp their usage effectively.
Regular vs. Irregular Verbs in English
Comparing the proportion and learning difficulty of verb types:
Regular Verbs
Examples and Usage
Regular verbs follow a predictable pattern. You form the past tense by adding -d or -ed. This consistency makes them easier to learn and use. Here are some examples:
- Walk: You say, "I walk to school every day."
- Play: You express, "I play soccer on weekends."
- Talk: You state, "I talk to my friends often."
These verbs illustrate how regular verbs maintain a straightforward structure. You can easily transition them into the past tense by following the rule.
Irregular Verbs
Examples and Usage
Irregular verbs do not follow standard rules. They require memorization because their forms change unpredictably. Here are some examples:
- Go: You say, "I go to the gym regularly."
- Have: You express, "I have breakfast at 8 AM."
- Do: You state, "I do my homework after school."
Irregular verbs demand more attention due to their unique forms. Despite this, they are crucial in everyday language.
Scientific Research Findings: Studies show that irregular verbs dominate in students' writing. They are stored in lexical memory, unlike regular verbs, which rely on compositional processing.
Mastering both regular and irregular verbs enhances your ability to express actions clearly. You can then explore more complex structures like the Perfect Tense. The Present Perfect Tense, for example, combines the present and past, offering a nuanced way to describe actions.

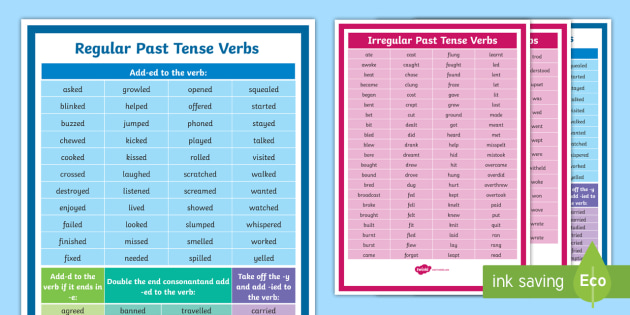
List of Past Tense Words

Understanding past tense verbs is crucial for narrating events that have already happened. You use them to describe completed actions, providing a clear timeline in your communication. This section offers a concise list of regular and irregular verbs, helping you grasp their usage effectively.
Regular Verbs
Examples and Usage
Regular verbs follow a predictable pattern. You form the past tense by adding -d or -ed to the base form. This consistency simplifies learning and application. Here are some examples:
- Walked: You say, "I walked to the library yesterday."
- Played: You express, "I played basketball last weekend."
- Talked: You state, "I talked to my teacher after class."
These verbs illustrate how regular verbs maintain a straightforward structure. You can easily transition them into the past tense by following this rule.
Irregular Verbs
Examples and Usage
Irregular verbs do not adhere to standard rules. They require memorization because their forms change unpredictably. Here are some examples:
- Went: You say, "I went to the museum last Saturday."
- Had: You express, "I had breakfast at 7 AM."
- Did: You state, "I did my homework last night."
Irregular verbs demand more attention due to their unique forms. Despite this, they are essential in everyday language.
Scientific Research Findings: Studies indicate that irregular verbs dominate in students' writing. They are stored in lexical memory, unlike regular verbs, which rely on compositional processing.
Mastering both regular and irregular verbs enhances your ability to express actions clearly. You can then explore more complex structures like the Perfect Tense. The Past Perfect Tense, for example, offers a nuanced way to describe actions that occurred before another past event.
Tips for Practicing Verb Tenses
Mastering verb tenses requires consistent practice. You can enhance your skills through various exercises and resources. This section provides practical tips to help you improve your understanding of verb tenses, including the Continuous Tense and Future Continuous Tense.
Effective Verb Tense Learning Process
Follow this step-by-step approach to master verb tenses:
flowchart TD
A[Start Learning] --> B[Understand Basic Rules]
B --> C[Memorize Common Examples]
C --> D[Practice Writing Exercises]
D --> E[Engage in Speaking Practice]
E --> F[Get Feedback]
F --> G[Review Mistakes]
G --> H[Apply in Real Contexts]
H --> I[Regular Review]
I --> J[Master Verb Tenses]
style A fill:#FF8000,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
style J fill:#FF8000,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px
Practice Exercises
Writing Exercises
Writing exercises are essential for reinforcing your knowledge of verb tenses. You can start by crafting sentences using different tenses. For example, write a paragraph describing your daily routine in the present tense. Then, rewrite it in the past tense. This exercise helps you see how verbs change with time. Additionally, try writing short stories that incorporate the Future Continuous Tense. This will challenge you to think about actions that will be ongoing in the future.
Speaking Exercises
Speaking exercises allow you to practice verb tenses in real-time. You can describe your day to a friend, focusing on using the Continuous Tense. For instance, say, "I am walking to the store," or "I was walking to the store." This practice helps you become more comfortable with verb forms. You can also engage in role-playing activities where you discuss future plans using the Future Continuous Tense. For example, "I will be studying for my exams next week."
Resources for Further Learning
Online Tools
Online tools offer interactive ways to practice verb tenses. Websites like Grammarly and QuillBot provide exercises and quizzes to test your knowledge. These platforms often include explanations and examples, helping you understand the nuances of each tense. You can also find apps that focus on specific tenses, such as the Continuous Tense, allowing you to practice anytime, anywhere.
Books and Guides
Books and guides serve as valuable resources for learning verb tenses. You can find grammar books that offer detailed explanations and exercises. Look for guides that include sections on the Future Continuous Tense and other complex structures. These resources often provide examples and practice questions, helping you solidify your understanding. Additionally, consider using workbooks that focus on verb conjugation and sentence construction.

Mastering verb tenses is essential for clear communication. You enhance your language skills by practicing regularly. Remember, understanding the Future Perfect Tense and Future Perfect Continuous Tense will further enrich your expression. If you are a teacher and you want to impart these useful examples more effectively to your students, all you need is a perfect PowerPoint presentation. I recommend using PageOn.ai, which is an AI-driven intelligent tool that can convert various formats into PPTs. It automatically recognizes file content and generates the PPT you desire. If you lack creative ideas, simply enter the topic you want, and PageOn.ai can automatically generate the content you need. This tool will be of great assistance in your educational work.
You Might Also Like
The Art of Instant Connection: Crafting Opening Strategies That Captivate Any Audience
Discover powerful opening strategies that create instant audience connection. Learn visual storytelling, interactive techniques, and data visualization methods to captivate any audience from the start.
Mastering FOMO Psychology: Creating Irresistible Business Pitch Strategies | PageOn.ai
Learn how to leverage FOMO psychology in your business pitches to drive urgent action. Discover proven strategies for creating authentic scarcity, exclusivity, and urgency that converts.
Mastering Workplace Communication with International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) - Visual Guide
Discover how the International Phonetic Alphabet transforms workplace communication. Learn visual approaches to implement IPA for clearer global business interactions.
From What to Why in Business Presentations: Purpose-Driven Storytelling Strategy
Transform your business presentations from data-heavy information delivery to purpose-driven storytelling that engages audiences and drives decisions with these expert strategies.